-
 System CertificationZOHOCERT establishes trust with excellent quality, conveys trust with the concept of Zhongzheng, and enhances customers' ability to respond to risks and...
System CertificationZOHOCERT establishes trust with excellent quality, conveys trust with the concept of Zhongzheng, and enhances customers' ability to respond to risks and... -
 Product CertificationZOHOCERT establishes trust with excellent quality, conveys trust with the concept of Zhongzheng, and enhances customers' ability to respond to risks and...
Product CertificationZOHOCERT establishes trust with excellent quality, conveys trust with the concept of Zhongzheng, and enhances customers' ability to respond to risks and...
-
 Public DocumentsZOHOCERT establishes trust with excellent quality, conveys trust with the concept of Zhongzheng, and enhances customers' ability to respond to risks and challenges, as well as their sustained commercial value, to win trust!
Public DocumentsZOHOCERT establishes trust with excellent quality, conveys trust with the concept of Zhongzheng, and enhances customers' ability to respond to risks and challenges, as well as their sustained commercial value, to win trust! -
 Case PresentationZOHOCERT establishes trust with excellent quality, conveys trust with the concept of Zhongzheng, and...
Case PresentationZOHOCERT establishes trust with excellent quality, conveys trust with the concept of Zhongzheng, and...


Certification Description
■ISO26262 road vehicle functional safety management system certification
With the increasing complexity of the automotive industry, automotive companies have increased their efforts to develop automotive safety compliance control systems. ISO 26262 is a uniform safety standard for automotive electrical and electronic systems. ISO 26262 provides a common standard for measuring the safety of automotive electrical and electronic systems in use. ISO 26262 is voluntary implementation, but under the increasingly severe policy and industry trends, both automobile manufacturers and parts suppliers should adjust the system as soon as possible in order to meet the requirements of ISO 26262 and build a management system process based on ISO 26262. ISO26262 will empower your credibility in the field of automotive safety, making you more worthy of trust and trust.
■ISO 26262 certification process
Contract Signing Project Communication Preparation Gap Analysis Standard Training Process Planning Process Review Issue Certificate
■Certification Standards
ISO 26262-1:2018 Road vehicles-Functional safety-Part 1: Vocabulary road vehicles-Functional safety-Part 1: Terminology
ISO 26262-2:2018 Road vehicles-Functional safety-Part 2: Management of functional safety-Road vehicles-Functional safety-Part 2: Functional safety management
ISO 26262-3:2018 Road vehicles-Functional safety-Part 3: Concept phase Road vehicles-Functional safety-Part 3: Concept phase
ISO 26262-4:2018 Road vehicles-Functional safety-Part 4: Product development at the system level Road vehicles-Functional safety-Part 4: Product development: System level
ISO 26262-5:2018 Road vehicles-Functional safety-Part 5: Product development at the hardware level Road vehicles-Functional safety-Part 5: Product development: Hardware level
ISO 26262-6:2018 Road vehicles-Functional safety-Part 6: Product development at the software level Road vehicles-Functional safety-Part 6: Product development: Software level
ISO 26262-7:2018 Road vehicles-Functional safety-Part 7: Production, operation, service and decommissioning road vehicles-Functional safety-Part 7: Production, operation, service and scrapping
ISO 26262-8:2018 Road vehicles-Functional safety-Part 8: Supporting processes road vehicles-Functional safety-Part 8: Supporting procedures
ISO 26262-9:2018 Road vehicles-Functional safety-Part 9: Automotive safety integrity level (ASIL)-oriented and safety-oriented analyses road vehicles-Functional safety-Part 9: Automotive safety integrity level-oriented and safety-oriented analysis
ISO 26262-10:2018 Road vehicles-Functional safety-Part 10: Guidelines on ISO 26262 Road vehicles-Functional safety-Part 10: ISO26262 guidelines
■ZOHOCERT
Is a professional service organization that has been deeply involved in the IT information industry for many years.
Has a number of senior academic management experts with more than 20 years of practical experience.
High-quality IT expert team services with a nationalized vision
Scope of Certification
Road Vehicle Functional Safety Management Systemcertification business scope
Certification standards: GB/T 33529-2017
| ISO26262-BMS | Battery Management System |
|---|---|
| ISO26262-MCU | micro control unit |
| ISO26262-ECU | Electronic Control Unit |
| ISO26262-ABS | Automobile Anti-lock Braking System |
| ISO26262-BAS | Brake Assist System |
| ISO26262-TPMS | Tire pressure real-time monitoring system |
| ISO26262-PEPS | Keyless Entry System |
| ISO26262-ESP | Body Stability Control System |
| ISO26262-EPS | Electronic Power Steering System |
| ISO26262-CCAS | Automotive Anti-collision Radar System |
| ISO26262-AFS | adaptive front lighting system |
| ISO26262-LDWS | Lane Departure Warning System |
| ISO26262-ASR | Traction control system |
| ISO26262-EBD | Electronic Brake Force Distribution System |
| ISO26262-EBA | Emergency Brake Assist System |
| ISO26262-VSC | Body Stability Control System |
| ISO26262-PAS | Parking assist system |
| ISO26262-Seat-belt | Seat belt pre-tensioning |
| ISO26262-Electronic | Electronic brake system |
| ISO26262-Electric Vehicle (EV) | vehicle control system hardware and software |
| ISO26262-Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV) | vehicle control system hardware and software |
Certification Scheme
a new car, no matter how advanced driving functions are integrated, designers need to provide sufficient evidence to prove that the newly added functions have sufficient safety to meet the requirements of vehicle safety.
With the electrification and intelligence of vehicles, vehicle electrical andelectronicsystem also increases. The increase in the complexity of electronic/electrical systems has brought about an increase in the risk of system failure and random failure, and the resulting uncertainty of automotive safety, which has become the biggest challenge on the road to the transformation of automotive intelligence today.
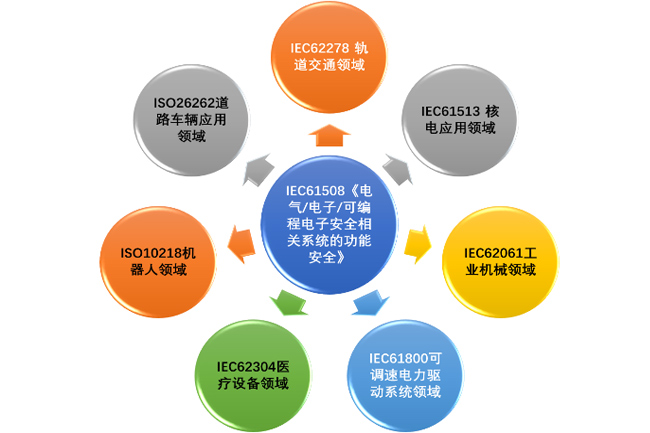
In 2011, the International Organization for Standardization Road Vehicle Technical Committee sorted out the special safety of the electrical/electronic system of "road vehicles" based on the IEC61508 (first published in 2000), and proposed electrical/electronic hardware and software related to the functional safety of vehicles. And the safety requirements and verification requirements of related components in the whole life cycle of design, production, service and scrapping. ISO26262 "road car functional safety" was officially born. At present, ISO26262 certification is a necessary condition for products to enter the supply chain system of automotive electronic/electrical components and systems.
2. ISO26262
ISO26262 provides corresponding safety assurance measures for ensuring the functional safety of the electronic/electrical system in the whole life cycle of the vehicle (including product development, production, use, maintenance and scrapping), such as how to evaluate/improve/verify the safety requirements, methods and control processes, and also provides a safety assurance framework including mechanical, hydraulic, pneumatic and other technologies.
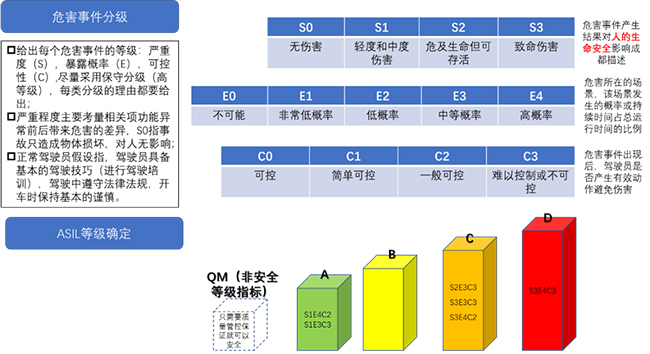
ISO26262 from the perspective of vehicle functional safety, through the hazard analysis of functional related items, risk assessment, determine the vehicle safety integrity level (ASIL), and then determine the safety objectives.
subdivides the functional related items, the electronic/electrical systems that make up the related items, the components that make up the system, and the components that make up the components. The corresponding functional safety concepts and technical safety concepts are formulated for each level, and the safety of the related items is evaluated through review, verification and other means.
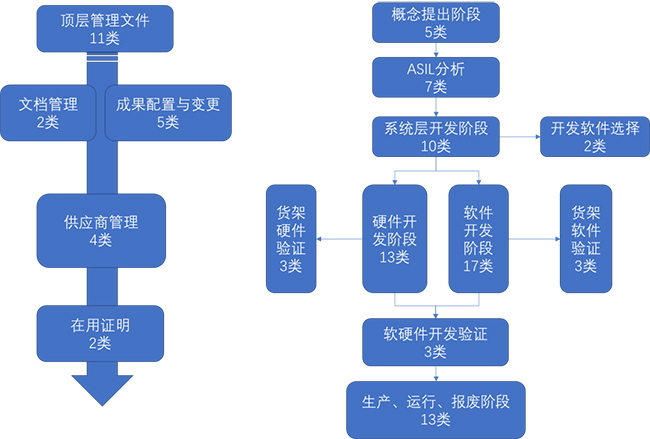
review generally reviews the work results (walk-through/inspection/approval review) formed by the work done to achieve relevant safety objectives during the system development process. The work results include about 86 types of result documents, covering documents of functional safety activities in the whole life cycle from the product concept proposal stage to scrap, as well as management documents of developers and suppliers.
For the development and manufacture of electronic components and components, ISO26262 provide corresponding safety certification guidelines. Electronic assemblies or components specifically developed for ISO26262 shall be developed and validated in accordance with ISO26262-5 development requirements safety activities.
, for shelf electronic components or components, the development stage does not introduce ISO26262 safety concepts, and safety function assessment and risk assessment of deviation from safety objectives need to be carried out according to the ISO26262-8's evaluation requirements for hardware elements. When evaluating such shelf electronic components and components, they are classified according to the characteristics of the product, the difference in evaluation difficulty, and the role of the elements in the safety concept (Class I-Class III).
3. Class Ⅰ-Class Ⅲ
ClassⅠ
Class I components or components belong to the simplest certification elements (collectively referred to as electronic components/components), passive components and discrete devices belong to such elements, common characteristics of less working mode, working parameters can be fully evaluated and there is no internal fault diagnosis and control mechanism.
in the ISO26262-11-2011 version, such evaluated elements only need to be certified by the ISO16750 or AEC-Q corresponding standards, while in the 2018 version, such elements do not need to be individually evaluated, but can be evaluated at a higher integration level.
ClassⅡ
Class II elements are characterized by a variety of working modes, but they also do not have internal safety diagnosis and control mechanisms, such as sensors. Integrated circuits without integrated IP cores belong to such elements. The evaluation of such elements shall be carried out according to the ISO26262-8 adoption analysis (analysis of data, documents, models and records) and testing (test verification for the safety of functions and use environment), and the robustness test of the evaluated elements to external stress shall be evaluated according to the ISO26262-5.
assessment is to analyze and verify that the functional performance of the element meets its specifications and its intended use. These performance requirements shall fully consider the performance requirements of the evaluated elements under normal environment and the environment causing the failure.
ClassⅢ
Class III elements are characterized by a variety of working modes, and their functional performance can only be evaluated under consideration of actual working conditions. Internal embedded safety diagnosis and control mechanisms, such as MCU, DSP, and integrated circuits with integrated IP cores, belong to such elements. The evaluation of Class III elements is the most complex and demanding. In addition to meeting the requirements of Class II element safety evaluation, additional evaluation measures are required to show that the risk of deviation from safety objectives and safety requirements is low enough. Additional assessment measures include, but are not limited:
a) It is necessary to complete the verification of safety-related functions according to the specific use function and use environment.
B) It is best to have a usage history of similar usage scenarios as a supporting basis for hardware security assessment.
c) The hardware should have independent and diversified cores to perform diagnostic functions, which can monitor the security of the chip.
d) The hardware development process implements certain safety standards, and the safety standards are equivalent to the ISO26262 ASIL level.
is not recommended. It is hoped that such elements can be upgraded in full accordance with the development requirements of the ISO26262-5 hardware layer in future upgrades.
ISO26262-2018 version adds ISO26262-11 "Semiconductor Development Guide", which provides methods and use cases for the development process of semiconductor components and components.
Certification Fees
Certificate Sample










